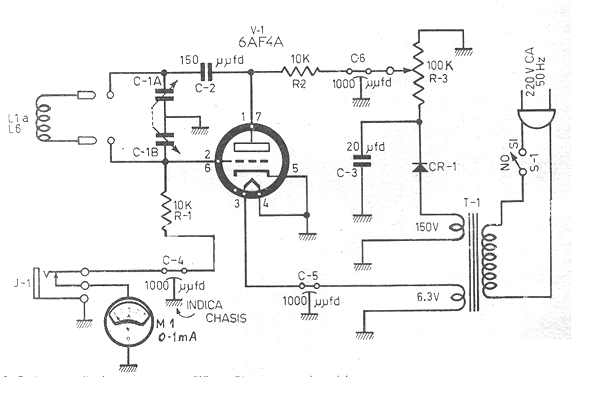
With the circuit shown it is possible to check the oscillator operation, determine the resonance frequency of LC circuits and more. The diagram was obtained from a 1972 documentation and uses a single valve. The operating principle lies in the variation that the grid current of an oscillator circuit suffers when the resonant frequency is reached, decreasing sharply. The name grid-dip (grid dip) comes precisely from this fact.
In assembly, the critical component in addition to the tube is the transformer. The coils, wrapped in cardboard or plastic tubes with turns that vary between 10 and 100 turns, will typically cover the 1 MHz to 30 MHz range. The variable capacitor is of the two-section type found in old tube receivers.