The idea of Nicola Tesla was that the wires could be abolished and the power would be transmitted throughout space. In order to do so Nicola Tesla began working on several projects, standing out a huge transmitter that operates with high voltage (Tesla coil), as shown in Figure 1.
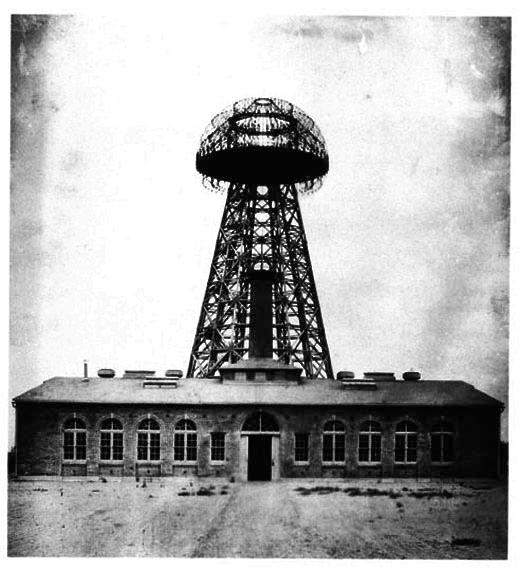

The idea of Tesla is nowadays called Wireless Power Transfer or WPT which surfaces with its application still short distance on direct applications such as mobile battery chargers and other electronics.
The transmission of energy throughout space has huge problems to be overcome.
The first is the dispersion of energy. If we think, for example, the use of light for the transmission, we notice that it disperses a few meters from the transmitter, the amount captured is too reduced.
The same occurs with the radio waves, for example, a beam of microwaves.
The LASER is a possibility, but it faces the danger that the beam of high energy can be inadvertently cut by a person or a vehicle and then a disaster may occur.
For short distances, where we should begin, there is the possibility of a more efficient and capacitive coupling, an inductive coupling.
It is the working principle of mobile chargers that we described in pther article in this site.
The operating principle is the same of the transformer.
We have a coil in the charger that transmits a signal, an average frequency current, and on the mobile phone, or on another device to be loaded, a second coil which works as the secondary of the transformer, as shown in Figure 2.
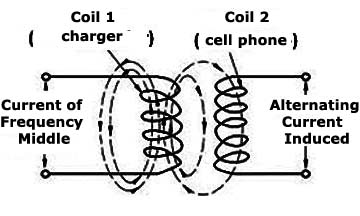
However, the large energy dispersion that occurs by the scattering of the line shape of the transmitter field causes the system to have only a very short distance performance.
The mobile phone, or another device to be loaded must be very close to the charger coil, as shown in Figure 3.

Regarding initially the inductive and capacitive systems are the most suitable for the practical applications we can develop a features table.
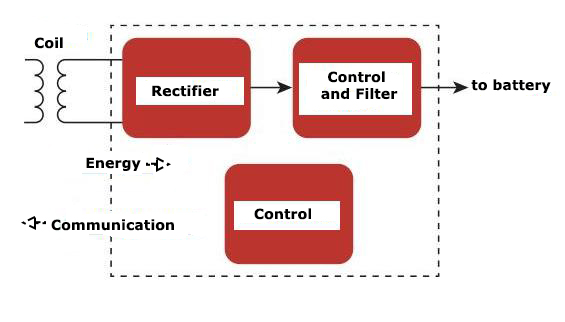
Figure 4 is a typical wireless charger circuit on the receiving party.
Challenges
The idea of the direct removal of the wires start to have a great adoption in mobile phones that will soon stop using connecting wires for this purpose.
Most new mobile phone models already have wireless charging capabilities, simply supporting them on the charger.
In the car itself, the charger connected to the cigarette outlet has already been eliminated by simply supporting the phone on the charger, as shown in Figure 5.

However, some problems may be overcome when considering a wireless charger in a noisy environment such as a car.
One of them is the interference (EMC) which may occur and affect the circuit performance. Moreover, the very power transmitter circuit produces radiation which can affect the car circuits.
Another problem is the variation in temperature the inside a car reaches high values.
However, all this already have solutions and the wires are being eliminated until they become a thing of the past.




