The electric properties of a PN junction can be used in devices other than the LEDs. Many special diodes can be included in a list:
A. Photodicdes: Exposing the PN junction of a diode to light and reverse-biasing it, the current flow will depend on the amount of light falling on the junction region. Charge carriers are liberated by the light, increasing the reverse current. The semiconductor material with a PN junction is then manufactured in transparent enclosures and used as light or IR sensors. These devices are called photodiodes.
B. Tunnel diodes: Tunnel diodes are special devices presenting the characteristic of a curve in a negative resistance region. This characteristic makes the device ideal to produce very high-frequency signals. The tunnel diode is used as µHF (Ultrahigh Frequency) and SHF (Superhigh Frequency) oscillators and detectors in many applications like radar detectors.
C. Varicaps or varactors: When reverse-biased, a diode can be compared with a capacitor. The junction region is the dielectric and the PN materials with the plates as shown in Figure 1.
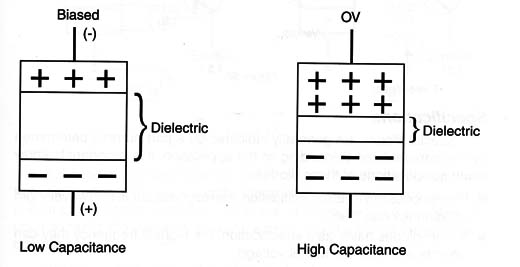
Depending on the applied voltage, the size of the junction region can be altered. If a low voltage is applied, the charges keep the junction region thinner. But, by increasing the voltage, the charges make the junction region fatter. This means that by applying a voltage in a reverse-biased diode we can control its capacitance.
Special diodes with large PN junctions (to get more capacitance) are fabricated to be used as variable capacitors controlled by voltages. They are called variable capacitance diodes or Varicaps. These capacitors are found in tuning circuits of TVs and radios.
Symbols and Types
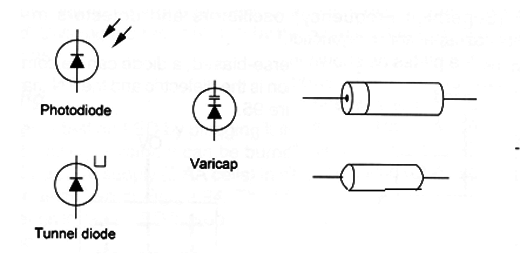
Figure 2 shows the symbols and types of some special diodes. Remember that these diodes are also polarized components and some mark is used to the identification of their poles.
Specifications
Special diodes are generally indicated by a part number determined by the manufacturer. Depending on the application, it is important to know some specifications of these diodes.
- Photodiodes have, as a specification, the response curve (the wavelength of light they can “see”).
- Tunnel diodes have, as a specification, the highest frequency they can operate and also the tunnel voltage.
- Varicaps can be specified by the capacitance range they can present between zero and a nominal voltage.
Testing
The test of many special diodes cannot be done using simple procedures. We can detect if a photodiode, tunnel diode or varicap diode is shorted or open, but not determine any other important characteristics of these components, such as wheater they are operating, for example.




