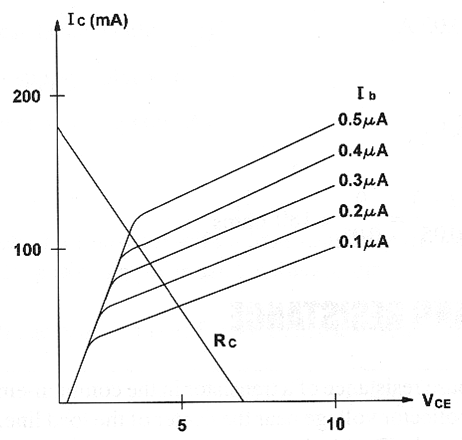
The load resistance of a transistor depends on the power supply voltage, the voltage between collector and emitter and also on the amount of current flowing to the collector. Figure bellow shows the typical family of characteristic curves of a transistor and the basic circuit to calculate the load resistance using the following formula.
Formula 1
Load resistance:
Rc = ( Vb – Vce ) / Ic
Where:
Rc is the load resistance in ohm (Ω)
Vb is the power supply voltage in volts (V)
Vce is the voltage between collector and emitter in volts (V)
Ic is the collector current in amperes (A)
Application example:
In a circuit a transistor must operate in the next conditions: voltage between collector and emitter = 3.0 V; collector current = 50 mA; power supply voltage = 12 V.
Data:
Vce = 3.0 V
Ic = 50 mA = 0.05 A
Vb = 12 V
Rc = (12 – 3) / 0.05
Rc = 9 / 0.05
Rc = 180 Ω




