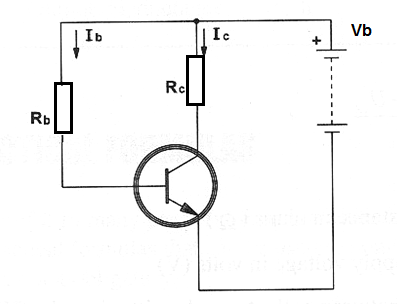
When calculating the base resistance of a transistor in the common emitter configuration as shown it is important to keep the collector voltage near the center of the load line as shown in the next figure to avoid distortion of signals. The biasing resistance will depend on the power supply voltage and the base current.
Formula 1
Base resistor:
Rb = Vb / Ib
Where:
Rb is the base resistance on ohm (Ω)
Vb is the power supply voltage in volts (V)
Ib is the base current in amperes (A)
Application example:
Find the base resistance to a transistor with a load resistance of 1 kΩ and with a collector current of 10 mA. A 12 V power supply is used in this circuit.
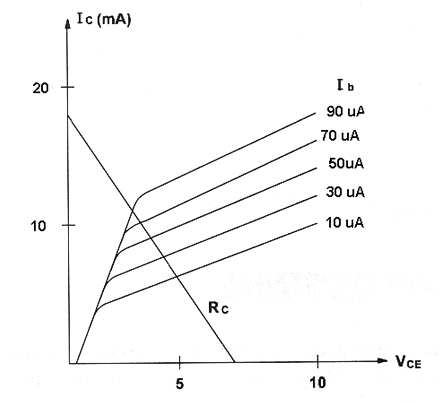
Figure bellow shows the characteristic curves for the used transistor.
Data:
RL = 1 000 Ω
Ic = 10 mA = 0.01 A
Ub = 12 V
From the characteristic curves we can see that when the collector current is 10 mA the current flowing to the base is 50 µA.
Applying formula 1:
Rb = 12 / (50 x 10-6)
Rb = (12 / 50) x 106
Rb = 0.24 x 106
Rb = 240 kΩ




