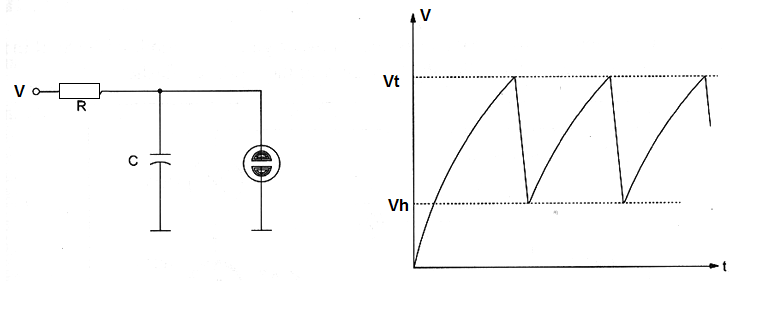
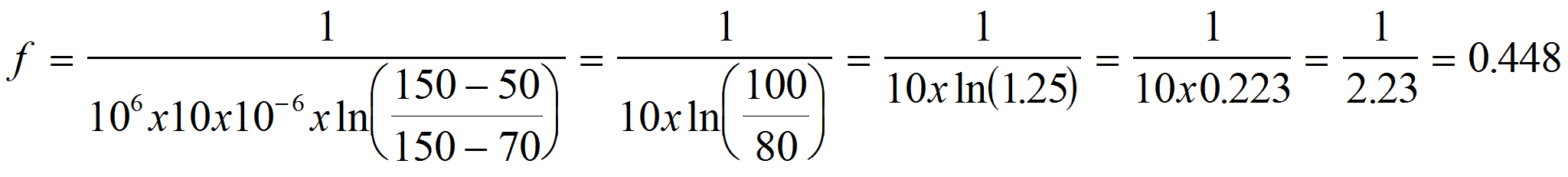Figure shows the basic configuration of a relaxation oscillator using a neon lamp. This circuit is suitable to frequencies up to some tens quilohertz and operates from power supply voltages over 80 volts.
A typical neon lamp breakes down at 70 V and establishes a glow and this glow is extinguished when the voltage accross the lamp is reduced to 50 V. The next formula is valid to these parameters.
Formula 1
Period:
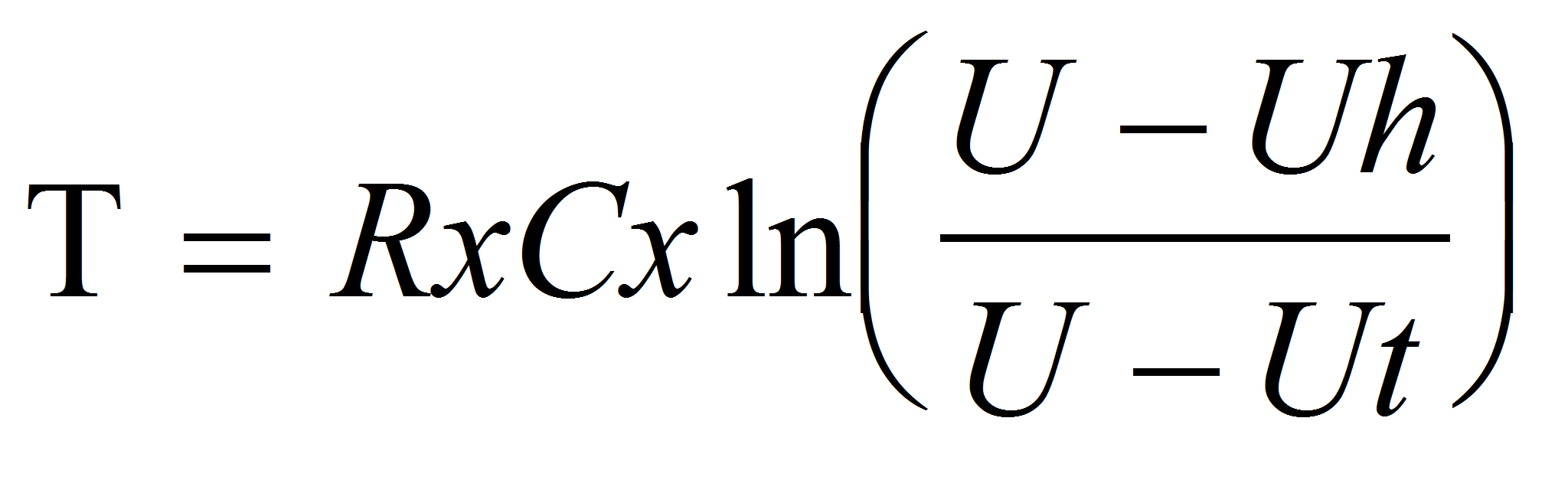
Where:
T is the period in seconds (s)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
U is the power supply voltage in volts (V)
Ut is the triggering voltage in volts (V) - 70 V typ.
µH is the holding voltage in volts (V) - 60 V typ.
Formula 2
Frequency:
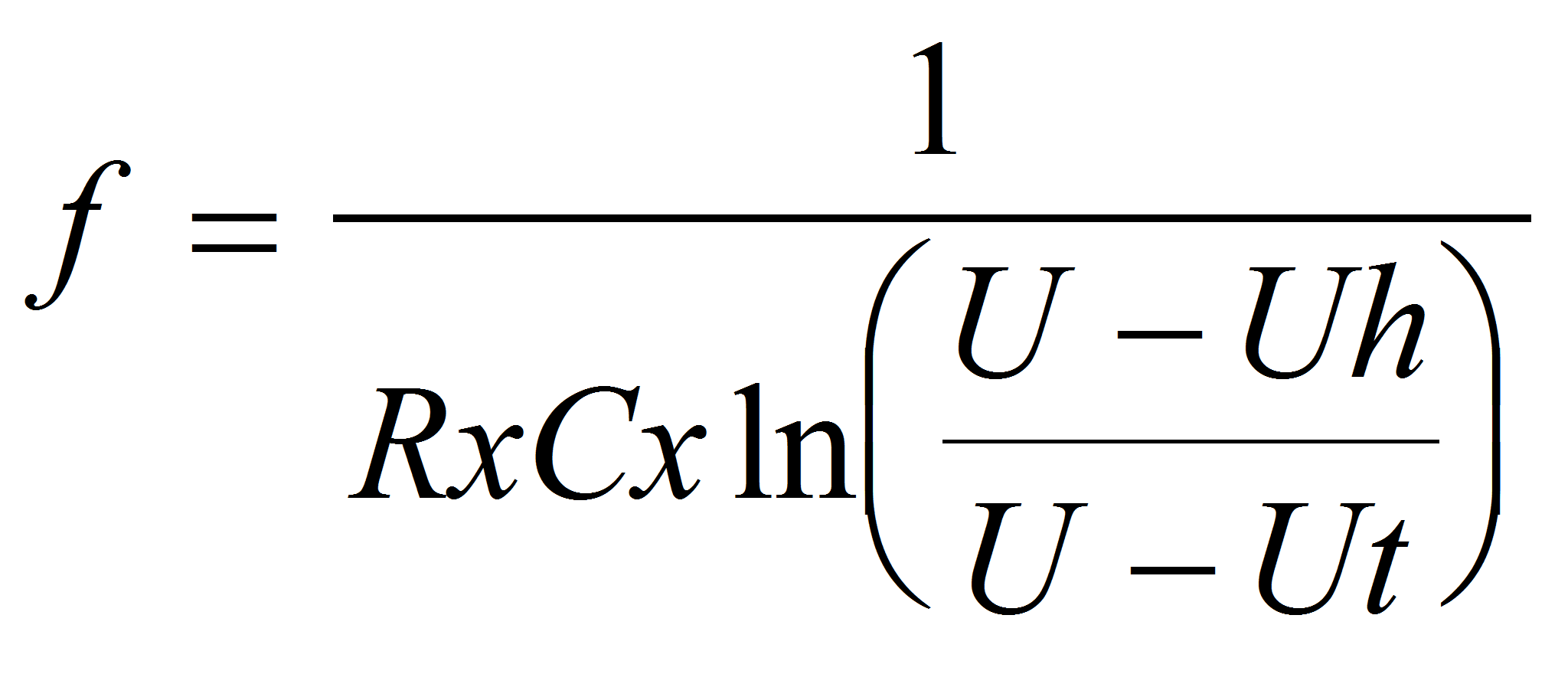
Where:
f is the frequency in hertz (Hz)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
U is the power supply voltage in volts (V)
Ut is the triggering voltage in volts (V)
µH is the holding voltage in volts (V)
Application example:
In the circuit shown in figure bellow the resistance between gate and cathode of the SCR in the on state is not considered. Determine the frequency of the produced flashes:
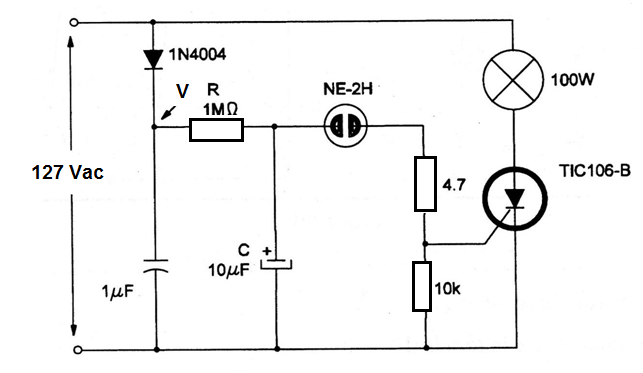
Data:
R = 1 MΩ = 106 Ω
C = 10 µF = 10 x 10-6 F
U = 150 V
Ut = 70 V
µH = 50 V
f = ?
Applying formula 2: