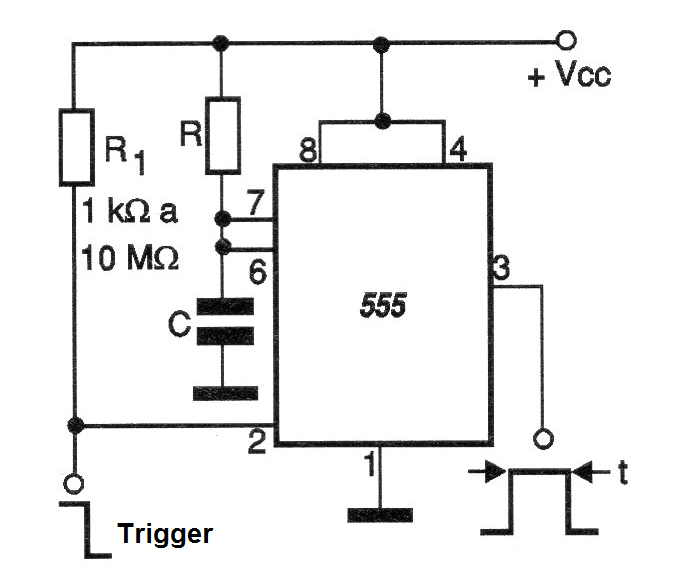
When connected as a monostable multivibrator the 555 needs an external trigger command applied to the trigger input (pin 2) to start the action. This is normally done by leaving the trigger input positive and by a moment putting it to to ground. By this the output goes to the high logic level (positive) by a time interval that can be calculated by the next formula. Figure bellow shows the 555 in the monostable configuration.
Formula
Time on:
T = 1.1 x R x C
Where:
T is the period or time on in seconds (s)
R is the resistance in ohm (Ω)
C is the capacitance in farads (F)
TABLE - Limit Values For The Monostable 555
| Parameter/Component | Limit Value |
| R max | 3 MΩ |
| R min | 1 kΩ |
| C max | 2 000 µF (*) |
| Cmin | 500 pF |
| Tr(max) | 1/4 T |
| Iout (drain or source) | 200 mA |
| Vcc | 18 V |
(*) depends on leakage.
Where:
Iout is the maximum output current
Vcc is the power supply voltage
Tr is the trigger pulse duration in seconds
GRAPH - 555 Monostable - On time versus R and C
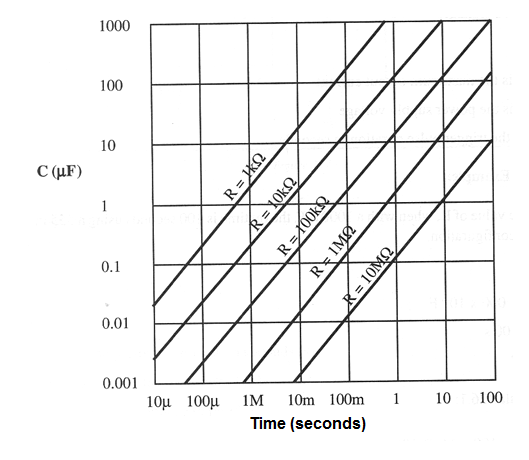
Application example:
Calculate the value of R to have with a 1 000 µF a time on of 100 seconds using a 555 in the monostable configuration.
Data:
C = 1 000 x 10-6 F
T = 100 s
R = ?
Using formula 1:
100 = 1.1 x R x 1000 x 10-6
Isolating R:
R = 100 / ( 1.1 x 1000 x 10-6 )
Solving the equation:
R = (1000 x 103) / 1.1
R = 90.9 x 103
R = 90.9 kΩ




