The circuit runs in frequencies between 100 and 1,000 Hz, depending on the sensor and Cl value. You can alter C1 in a wide range of values to get different sounds from the oscillator. Values between 470 pF and 0.1 µF can be used for experimentation.
The output transducer is a piezoelectric device, but you can use powerful stages as shown in other projects. The circuit should be powered with voltage sources between 6 and 12 V, and it drains only a few milliamperes with the recommended output transducer.
Figure 1 shows the complete circuit of the touch-controlled oscillator.
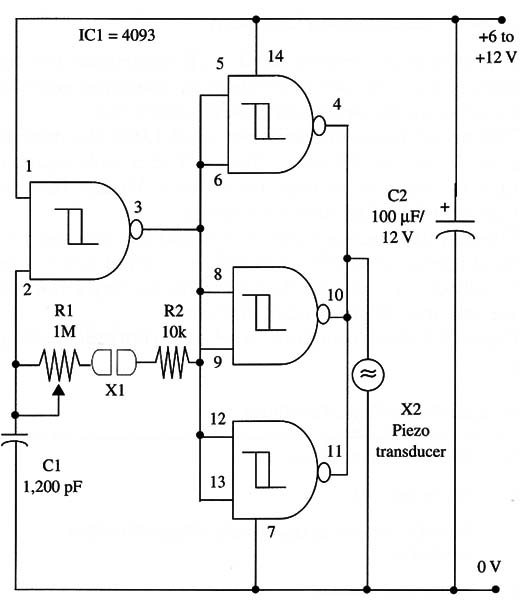
Two small plates or screws form the touch sensor. If you use a conductive foam or two metal plates as sensor, change C1 to a large value (between 0.022 and 0.047 µF) to get a pressure-controlled oscillator.
IC1 - 4093 CMOS integrated circuit
X1 - Sensor (see text)
X2 - Piezoelectric transducer or crystal earphone, Radio Shack 273-073 or equivalent
R1 - 1,000,000 ohm potentiometer
R2 - 10,000 ohm, 1/4 watt, 5% resistor
C1 - 1,200 pF ceramic capacitor
C2 - 100 µF, 12 WVDC electrolytic capacitor




