Obs. This project after be published in a Brazilian Magazine was included in my book CMOS Projects and Experiments (Newnes 1999)
C1 can be varied to change the range of the flash rate. Values between 100 and 1,000 µF can be used experimentally according the intended application.
The circuit consists of a variable duty cycle oscillator that drives an SCR. As its load, the SCR has a common incandescent lamp of from 5 to 200 W Remember that SCRs are half-wave devices that drive the loads with half of the total power.
A schematic diagram of the AC Lamp Flasher is given in Fig. 1.
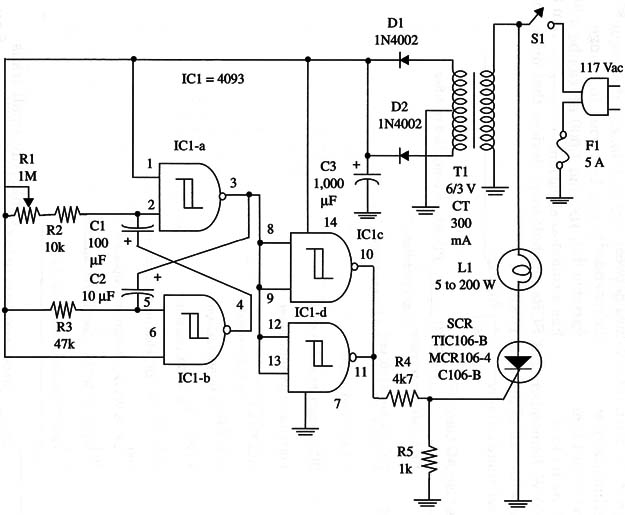
The SCR must be mounted on a heatsink. Any small transformer with its secondary rated from 300 to 500 mA can be used.
You can also alter this circuit for a full-wave control by inserting a full-wave bridge (200 V, 4 A diodes) in the load line. The flashes are adjusted by R1.
Note: this circuit operates only with incandescent lamps. Do not use with fluorescent or electronic lamps.
IC1 - 4093 CMOS integrated circuit
SCR - TIClO6, MCR106, or C106 200 V PIV silicon controlled rectifier
D1, D2 - 1N4002 or equivalent silicon rectifiers
T1 - 6.3 V, CT, 300 to 500 mA transformer
F1 - 5 A fuse and holder
S1 - SPST toggle or slide switch
R1 - 1,000,000 ohm - potentiometer
R2 - 10,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R3 - 47,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R4 - 4,700 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R5 - 1,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
C1 -100 µF, 16 WVDC electrolytic capacitor
C2 - 10 µF, 16 WVDC electrolytic capacitor
C3 -1,000 µF, 15 WVDC electrolytic capacitor
L1 - 5 to 200 W incandescent lamp, 117 V




