Time delays can be adjusted in a wide range of values, depending on the capacitor used. Time delays between a few seconds and a few minutes are easy to obtain. A mini DPDT relay (Radio Shack 279-07 9) controls external loads up to 100 W.
Heavy-duty relays can replace the original one, but you must also replace the output transistor with a Darlington. Currents up to 1 A can be controlled by this transistor using a 12 V power supply.
A schematic diagram of this timer is shown in Fig. 1.
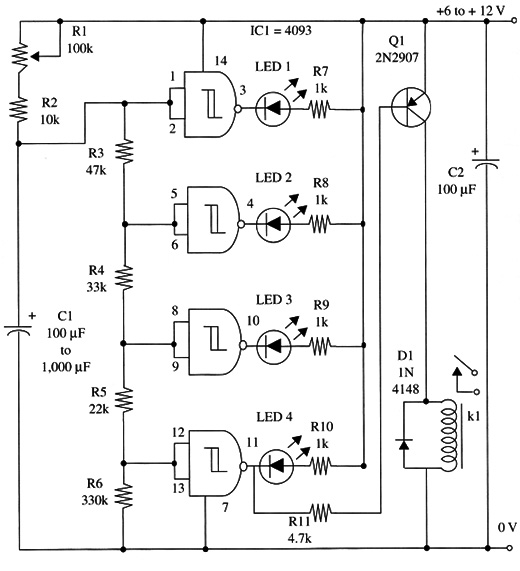
Positioning of the polarized components (LEDs, electrolytic capacitors, and diodes) must be correct. Note that a small SPST relay can be mounted directly on the solderless board or printed circuit board.
Other types of relays can also be used, but according to the case, they should not be mounted on a solderless board. Heavy-duty relays, Wit 100 to 500 mA coils, can be used by replacing driver transistor Q1 With a PNP Darlington transistor and using a 12 V power supply.
IC1 - 4093 CMOS integrated circuit
Q1 - 2N2907 NPN general purpose silicon transistor
D1 - 1N4148 general purpose silicon diode
LED1- LED4 Red common LEDs
K1 - 6 or 12 V relay, up to 100 mA (Radio Shack 27 5-249, 12 V, 43 mA, is a suitable unit)
R1 - 100,000 ohm potentiometer
R2 -10,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R3 - 47,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R4 - 33,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R5 - 22,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R6 - 330,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
R7 to R10 - 1,000 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistors
R11 - 4,700 ohm, 1/4 W, 5% resistor
C1 - 100 µF to 1,000 µF, 12 WVDC electrolytic capacitor
C2 - 100 µF, 12 WVDC electrolytic capacitor




